Reptiles are the next step up which helps because now they can develop an embryo away from land meaning they can distribute themselves to different places!
There are characteristics which these amniotes do have which are:
- Amniotic eggs

The embryos can be developed outside of water, and they can now become bigger in size and faster growing which is pretty crazy!
The allontois is a waste storage which contains the metabolic wastes and is heavily vascularized. They also permit gas exchange!
The yolk sac provides nutrient while the chorion surronds the membrane to also help with gas exchange. The shell is for structure and protection and this helps resist the egg to water loss.
When it is time for the hatchlings to exit they have an “egg tooth” which helps break through the hard shelled eggs. - Thicker, waterproof skin

The skin does not permit gas exchange at all but it does reduce dehydration.
The epidermis has become more keratinized therefore it became more rigid.
There are also other structures which contain keratin such as scales, feathers and hair. The hydrophillic lipids also helps with limiting water loss. - Rib ventilation of lungs
There is now increased surface area for gas exchange. There is negative pressure breathing where the air is sucks in due to the expansion of the thoracic cavity and it creates a negative vacuum. This is similar to humans.Inspiration: The external intercostals contract, diaphragm contracts and the chest wall expands
Expiration: The stenum and ribs contract and the diaphragm relaxes which causes the external intercostals to relax.
The internal intercostals only contract when there is active expiration. - Stronger jaws
There is now a more developed jaw muscles and a muscular tongue. - More efficient cardiovascular system
It is now higher pressure with improvements to make it efficient. There is more complete partitioning with higher blood pressure to help with pumping and faster distribution of blood.
The atrium is separated and there is a lot more septa in the ventricle to help separate the blood. - Water conserving excretory system
There is production or urea and uric acid instead of ammonia as a waste product, as the ammonia is toxic when there is minimal water.
There is also now an efficient kidney and/or bladder. - Expanded brain and sensory organs
There is now a large cerebrum and cerebellum, this helps with better integration of sensory information and more complex muscle control.
The cerebrum is part of the forebrain which helps with many complex functions such as navigation. The cerebellum is used for motor control and balance.
Division of Amniotes
This is based on the skull structure with 3 different structures such as:
- Anapsida
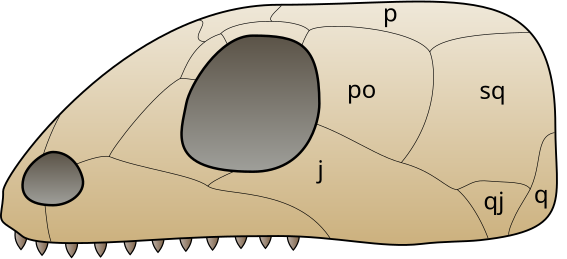
There is no openings behind occipital orbit (eye socket) - Diapsid
There are two temporal openings which are behind the occipital lobe. These openings may be for creating arches or allowing more muscles. - Synapsid

There is one temporal opening behind the occipital orbit, and this is the shape which led to mammals.
CLASS REPTILIA

I will be discussing the non-avian reptiles for now (birds will be in the next blog). These guys are ancestrally diapsid and they have B-keratin which forms hard keratin. They have 2 pairs of limbs and usually 5 digits which can be reduced or lost in some species.
They have tough dry scaly skin and are ectothermic which means they control their body temperatures by external means (e.g. convection via behavioural means).
Order Testudines

This is the order with turtles who appeared during the Triassic (200 million years ago) era. There are 325 species with a bony shell, keratinized plates instead of teeth and it is secondarily anapsid with the temporal openings lost.
BODY PLAN

The body is enclosed in a bony shell with the dorsal part being known as a carapace and the central part being known as a plastron.
There is an outer B-Keratin layer which is considered epidermal while there is an inner bone layers which has a fusion of ribs and vertebrae. The ribs has also become expanded.
They have their limb girdles located inside their rib age, and they are unable to expand their rib cage in order to breathe so they have to use their abdominal and pectoral muscles as a diaphragm! Insane!
They also don’t have teeth but they have a horn keratinised plate which is possibly from their younger days.
Sexy time?

They have internal fertilization and they are oviparous where they bury their eggs in the ground.
Some of the turtle species have temperature dependent sex where the lower temperatures between 18-27 degrees Celsius is male and higher temperatures means it is female.
This is odd at it could create not effective sex ratios in the populations.
Order Squamata
This suborder appeared during the Jurassic stage and radiated in the Cretaceous stage. This makes up 95% of the known non-avian reptiles.
They have a kinetic skull with moveable joints and new articulations (hinges) at the dorsal end of quadrants, palate and the roof of skull.
Suborder Sauria

These are the lizards which live in a range of different habitats. They usually have 4 limbs but some lack one or both pairs of limbs.
They also have moveable eyelids and external ears which is different to snakes.
Some examples include:
Gekko (Family Gekkonidae)

They are nocturnal and have invaginations on their foot to allow walking on the walls. They are also unable to see colour (no cones) and they have verticals eyeslits to close the eyes completely as it is very sensitive.
Iguanids (Family Iguanidae)

They have throat flaps!
Skinks (Family Scincidae)

They have reduced limbs.
Monitors (Family Varanidae)

Chameleons (Family chamaeleonidae)

They are able to change their colours rapidly and it is believed that it is for courtship.
They also can move the eyes independently of each other.
Amphisbaenia (Worm lizard)

This is a modified lizard who is a burrowed. It is able to move backwards and forward.
Suborder Serpentes
These guys are the snakes and they lack certain things including limbs, pectoral and pelvic girdles, ear openings or middle ear. They are still able to hear but in low frequencies.
The eye lids have also been fused over the eyes and an extremely kinetic skull. The half of the lower jaw is connected by skin and muscles which is able to spread widely, and there are many losely articulated skull bones to able asymmetrical flexing.
They have a shorter and wider vetebrae with increased numbers, which helps increase the lateral movement and they also have elongated neural spines. This can help with the side to side movement.
Most of them have enlarged transverse central scales to help prevent slipping.
Breathing may be heard when a snake is eating, so they have adapted a technique of thrusting forward the glottis (opening to trachea) between the mandibles. This allows breathing while they eat some pretty big animals.
They lack movable eyelids so they have created a “spectacle” which acts as a protective membrane.
SENSE ORGANS
The Jacobson’s organ are chemoreceptors which are paired puts on top of the mouth. They expose their tongue to the environment and then it helps them figure out the odours in the environment.
There are also pit organs which allow infrared radiation sensing, helping with localizations and detection.
Moving?
They move in lateral undulations and rectilinear motions (move contract fix stretch move).
Food time?
They are able to swallow the prey whole and some of them can attack their prey with the venom (20% of species).
Vipers are an example eighths I fangs being large and movable while they have a poison gland which is essentially modified saliva where they can inject their prey.
Some don’t have “true” fangs such as the Family Colubridae while some have small fangs such as the Family Elapidae.
.jpg) Colubridae includes the green tree snakes and brown tree snakes.
Colubridae includes the green tree snakes and brown tree snakes.
.jpg) Elapidae are the kind which sit and wait (Death Adders and Red bellied black snake).
Elapidae are the kind which sit and wait (Death Adders and Red bellied black snake).
Order Crocodilia
The crocodiles arose and radiated in the Mesozoic period. They have elongated skulls and thecodont (teeth).
The skulls have been reinforced and the jaw musculature is massive! This allows better chewing.
Their teeth is also located in the sockets which is the meaning of thecodont.
Heart
It is 4 chambered with the ventricles finally completely divided.
Alligators (Alligator mississipiensis)

They have a broad snout with the 4th tooth in notch.
Crocodiles (Crocodylus sp.)

The 4th tooth is completely visible and they have internal fertilization. They have high maternal care too.
Order Sphenodonta (Tuataras)

They arose and diversified in the early Mesozoic stage and are only found in New Zealand.
They are able to live up to 116 years and they are slow growing. They have a skull similar to the diapsids. They also have a well developed 3rd eye (only used as a baby and it called a parietal eye).
They are NOT LIZARDS.
So now that I have discussed this beautiful group I will move onto my favourites! The birds!!!
